Международный эндокринологический журнал Том 21, №4, 2025
Вернуться к номеру
Нутритивна терапія пацієнтів із серцево-судинними захворюваннями, стеатозом печінки та метаболічними розладами
Авторы: Fidel Krasniqi (1, 2), Afrim Zeqiraj (1, 2), Dafina Zeqiraj (2–4)
(1) - UBT Higher Education Institution, Department of Biochemistry, Prishtina, Kosovo
(2) - Policlinic and Laboratory Alpha, Peja, Kosovo
(3) - Regional Hospital, Peja, Kosovo
(4) - University of Tetovo, Faculty of Medical Sciences, Republic of North Macedonia
Рубрики: Эндокринология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
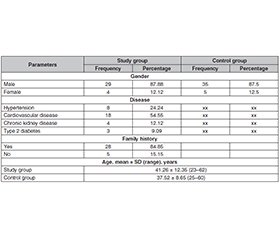
Актуальність. Серцево-судинні захворювання залишаються головною причиною смерті як чоловіків, так і жінок у промислово розвинених країнах. Вони охоплюють різноманітні стани, включаючи цереброваскулярні захворювання, захворювання периферичних артерій, атеросклероз і тромбоз глибоких вен. Неалкогольна жирова хвороба печінки (НАЖХП), яку також називають стеатотичною хворобою печінки, пов’язаною з метаболічною дисфункцією, характеризується наявністю макровезикулярного стеатозу без вираженого запалення. Мета: оцінити ефективність розроблених авторами харчових рекомендацій у пацієнтів із різними метаболічними розладами, включаючи серцево-судинні захворювання, НАЖХП, артеріальну гіпертензію, ожиріння й цукровий діабет 2-го типу. Матеріали та методи. Це дослідження проводилося на території Косово серед пацієнтів, які зверталися за лікуванням з приводу певних метаболічних розладів, i тривало з березня 2023 року по червень 2024 року. У ньому брали участь особи віком понад 18 років, пацієнтам основної групи було 23–62 роки, а контрольної — 25–60. Загалом було включено 73 пацієнти, з яких 33 увійшли до основної групи та 40 — до контрольної. Середній вік учасників становив 42,59 ± 12,05 року. Результати. Статистично значущі відмінності (p < 0,05) спостерігалися між основною та контрольною групами за кількома ключовими параметрами, як-от тригліцериди (TГ), ліпопротеїни високої щільності (ЛПВЩ), індекс маси тіла (ІМТ) та гомеостатична модель оцінки інсулінорезистентності (HOMA-IR). Крім того, вірогідні поліпшення (p < 0,05) були відзначені в основній групі після 3–6 місяців нутритивного лікування, зокрема за такими діагностичними параметрами: TГ, ЛПВЩ, аланінамінотрансфераза, ІМТ, HOMA-IR та вітамін D. Висновки. Наше дослідження демонструє, що рекомендоване нутритивне лікування привело до вірогідної позитивної динаміки в основній групі порівняно з контрольною.
Background. Cardiovascular diseases remain the leading cause of death in both men and women in industrialized countries. They encompass a variety of conditions, including cerebrovascular disease, peripheral arterial disease, atherosclerosis, and deep vein thrombosis. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), also referred to as metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease, is characterized by the presence of macro-vesicular steatosis without significant inflammation or alcohol consumption. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the health outcomes associated with the administration of supplements and dietary protocols, developed by the researcher, in patients with various metabolic disorders, including cardiovascular diseases, NAFLD, hypertension, obesity, and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Materials and methods. This study was conducted across the territory of Kosovo, targeting patients who sought treatment for specific health issues. The study period spanned from March 2023 to June 2024, involving participants aged over 18 years, with the main group aged 23–62 years and the control group aged 25–60 years. A total of 73 patients were included, with 33 in the study group and 40 in the control group. The average age of participants was 42.59 ± 12.05 years. Results. Statistically significant differences (p < 0.05) were observed between the study and control groups for several key parameters, including triglycerides (TGL), high-density lipoprotein (HDL), body mass index (BMI), and the homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR). Additionally, significant improvements (p < 0.05) were noted within the study group after 3–6 months of nutritional treatment, particularly in the following diagnostic parameters: TGL, HDL, alanine aminotransferase, BMI, HOMA-IR, and vitamin D. Conclusions. Our study demonstrates that the diet and nutritional supplements recommended by the researchers led to significant improvements in the study group compared to the control one (p < 0.05).
серцево-судинні захворювання; стеатоз печінки; цукровий діабет 2-го типу; харчові добавки; вітамін D; HOMA-IR
cardiovascular diseases; hepatic steatosis; type 2 diabetes mellitus; nutritional supplements; vitamin D; HOMA-IR
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- Rethemiotaki I. Global prevalence of cardiovascular diseases by gender and age during 2010–2019. Arch Med Sci Atheroscler Dis. 2023;8:e196-e205. doi: 10.5114/amsad/176654.
- Caturano A. Cardiovascular and Metabolic Disease: New Treatments and Future Directions 2.0. Biomedicines. 2024;12(6):1356. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12061356.
- Konkolÿ Thege B, Emmanuel T, Hill S, Wells L. Effectiveness of a complex psychosocial intervention to reduce metabolic syndrome in psychiatric outpatients with severe/persistent mental illness. Curr Psychol. 2023;42(12):9915-9924. doi: 10.1007/s12144-021-02269-3.
- Kobyliak N, Abenavoli L, Pavlenko G, Komisarenko Y. Gut microbiota composition changes associated with obesity: new lights from metagenomic analysis. Int J Endocrinol (Ukraine). 2020;16(8):654-661. doi: 10.22141/2224-0721.16.8.2020.222886.
- Jankovic N, Geelen A, Streppel MT, de Groot LC, Kiefte-de Jong JC, Orfanos P, et al. WHO guidelines for a healthy diet and mortality from cardiovascular disease in European and American elderly: the CHANCES project. Am J Clin Nutr. 2015;102(4):745-756. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.114.095117.
- Reddy VP. Oxidative stress in health and disease. Biomedicines. 2023;11(11):2925. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11112925.
- Pouwels S, Sakran N, Graham Y, Leal A, Pintar T, Yang W, Kassir R, et al. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): a review of pathophysiology, clinical management and effects of weight loss. BMC Endocr Disord. 2022;22(1):63. doi: 10.1186/s12902-022-00980-1.
- Tkach S, Pankiv V, Krushinska Z. Features of type 2 diabetes combined with metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver di–sease under conditions of chronic stress. Int J Endocrinol (Ukraine). 2024;20(1):18-24. doi: 10.22141/2224-0721.20.1.2024.1353.
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines on non-invasive tests for evaluation of liver disease severity and prognosis — 2021 update. J Hepatol. 2021;75(3):659-689. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.05.025.
- Sheka AC, Adeyi O, Thompson J, Hameed B, Crawford PA, Ikramuddin S. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a review. JAMA. 2020;323(12):1175-1183. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.2298.
- Dhande D, Dhok A, Anjankar A, Nagpure S. Silymarin as an antioxidant therapy in chronic liver diseases: a comprehensive review. Cureus. 2024;16(8):e67083. doi: 10.7759/cureus.67083.
- Gillessen A, Schmidt HH. Silymarin as supportive treatment in liver diseases: a narrative review. Adv Ther. 2020;37(4):1279-1301. doi: 10.1007/s12325-020-01251-y.
- Izzo C, Annunziata M, Melara G, Sciorio R, Dallio M, Masarone M, et al. The role of resveratrol in liver disease: a comprehensive review from in vitro to clinical trials. Nutrients. 2021;13(3):933. doi: 10.3390/nu13030933.
- Vik H. Highlighting the substantial body of evidence confirming the importance of vitamin K2 as a cardio-support nutrient, and how the right K2 makes all the difference. Integr Med (Encinitas). 2019;18(6):24-28.
- Yasutake K, Kohjima M, Kotoh K, Nakashima M, Nakamuta M, Enjoji M. Dietary habits and behaviors associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(7):1756-1767. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i7.1756.
- Wang H, Guo Y, Han W, Liang M, Xiao X, Jiang X, Yu W. Tauroursodeoxycholic acid improves nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by regulating gut microbiota and bile acid metabolism. J Agric Food Chem. 2024;72(36):20194-20210. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.4c04630.
- Song G, Weng F, Zou B, Zhao J, Jin J, Yan D, et al. Potential therapeutic action of tauroursodeoxycholic acid against cholestatic liver injury via hepatic FXR/Nrf2 and CHOP-DR5-caspase-8 pathway. Clin Sci (Lond). 2023;137(7):561-577. doi: 10.1042/CS20220674.
- Zeng P, Cai X, Yu X, Huang L, Chen X. HOMA-IR is an effective biomarker of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in non-diabetic population. J Int Med Res. 2023;51(10):3000605231204462. doi: 10.1177/03000605231204462.
- Gal R, Deres L, Toth K, Halmosi R, Habon T. The effect of resveratrol on the cardiovascular system from molecular mechanisms to clinical results. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(18):10152. doi: 10.3390/ijms221810152.
- Zhang X, Zhang Y, Sun A, Ge J. The effects of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide in cardiovascular diseases: molecular mechanisms, roles and therapeutic potential. Genes Dis. 2021;9(4):959-972. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2021.04.001.
- Calderon Martinez E, Herrera D, Mogan S, Hameed Z, Jangda AA, Khan TJ, et al. Impact of silymarin supplements on liver enzyme levels: a systematic review. Cureus. 2023;15(10):e47608. doi: 10.7759/cureus.47608.
- Schandelmaier S, Briel M, Saccilotto R, Olu KK, Arpagaus A, Hemkens LG, Nordmann AJ. Niacin for primary and secon–dary prevention of cardiovascular events. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;6(6):CD009744. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009744.pub2.